We refer to this problem as the vertex splitting problem. The replacement of a vertex by two copies as described in the exercise is called vertex splitting. The greedy algorithm performs a postorder traversal of the tree. During this traversal we compute, for each node
x, the maximum delay,
D(x), from x to any other node in its subtree.
If x has a parent z and
D(x) +w(z,x) exceeds
d, then the node x is split
and D(z) is set to 0.
Consider the example tree
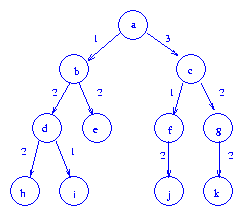
d = 3.
The delay, D(x), for x a leaf node
is 0.
So, D(x) = 0 when x
is any of the vertices {h, i, e, j, k}.
In postorder, a node is visited after its children have been.
When a node x is visited, its delay may be computed as:
D(x) = max{y is a child of x}{D(y) + w(x,y)}
So,
D(d) = 2.
Since D(d) + w(b,d) > d = 3,
we split node d to get the tree (a)
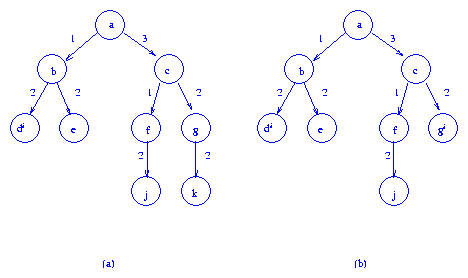
D(b) = 2 and D(f) = 2
are computed and since
D(b) + w(a,b) <= 3 and
D(f) + w(c,f) <= 3,
neither b nor f is split.
Then, since
D(g) = 2 and
D(g) + w(c,g) > d = 3,
node g is split and we get tree (b).
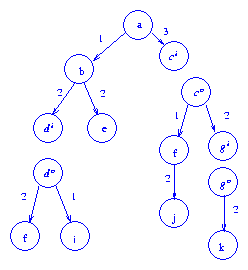
Next, node
c is visited and split since
D(c) + w(a,c) = 5 > 3 = d.
No more nodes are split.
The forest that results when the
three nodes d, g,
and c are split is given
below.
algorithm split(t)
{// split within the subtree with root t and compute D(t)
if (t != null)
{
// compute D(t)
D(t) = 0;
for (each child y of t)
{
split(y);
D(t) = max{D(t), D(y) + w(t,y)};
}
// split t if necessary
if (t.parent != null && D(t) + w(t.parent, t) > d)
{// split t
add t to S;
D(t) = 0; // for part that remains attached to parent
}
}
}
This algorithm assumes that
S has been
initialized to null
and that the weight
w(i,j)
of every edge (i,j)
is
<= d
since otherwise, there is no solution.
The complexity of the algorithm is O(n) where
n is the number of vertices in T.
split
finds a minimum cardinality S
such that T/S has no root-to-leaf path whose length
exceeds d.
This fact can be proved by induction on the number, n, of nodes
in the tree T.
If
n = 1, the claim is trivially valid.
Assume this claim is valid for n <= m
where m is an arbitrary natural number.
Let T be a tree with n + 1 nodes.
Let S be the set of vertices split by the greedy algorithm and
let W be a minimum cardinality vertex set such that
T/W has no root-to-leaf path whose length exceeds
d.
We need to show that |S| = |W|.
If |S| = 0, this is trivially true.
If |S| > 0, then let z
be the first vertex added to S
by the greedy algorithm.
Let Tz be the subtree of
T rooted at z.
As z is added to S by
the greedy algorithm, D(z) + w(z.parent, z) > d.
Hence, W must contain at least one vertex
u that is in Tz.
If W contains more than one such u,
then W cannot be of minimum
cardinality as Z = W - {all such u} + {z} is such that
T/Z has no root-to-leaf path whose length exceeds
d.
Hence, W contains exactly one such u.
Let W' = W - {u}.
Let T' be the tree that results from the
removal of the subtree Tz,
excluding node z,
from T.
If there is a W'' such that
|W''| < |W '|
and T'/W'' has no root-to-leaf pathwhose length
exceed d, then since
T/(W'' + {z}) has no root-to-leaf path whose length exceeds
d,
W is not a minimum cardinality splitting
set for T.
So, W' is a minimum cardinality vertex set such that
T'/W' has no root-to-leaf path whose length
exceeds d.
Also, S' = S - {z} is such that
T'/S' has no root-to-leaf path whose length exceeds
d. Furthermore S' is the
answer produced by split
when started with the root of T'.
Since the number of vertices in T'
is less than m + 1,
|S'| = |W'|.
Hence, |S| = |S'| + 1 = |W'| + 1 =
|W|.